In today’s world, companies + consumers alike are increasingly focused on sustainability metrics, like reducing carbon footprint + minimizing overall environmental impact. Staggeringly, the transportation sector alone accounts for 28% of total greenhouse gas emissions in the United States. However, freight rail is a lone wolf in the industry, and is the single most sustainable method of transporting goods across land. Despite handling roughly 40% of all US freight, railroads contribute only 1.9% of transportation-related greenhouse gas emissions. So what makes rail the greenest of the green? We’re glad you asked! Hop aboard + learn more as we share about all the ways railroads are striving for sustainability.
Move More with Less
Energy efficiency is one of the biggest reasons freight rail remains so sustainable. You may have seen this metric before – railroads are pretty proud of it, and we can’t blame them – on average, railroads can move one ton of freight nearly 500 miles on just a single gallon of fuel. That’s not only impressive, it is almost mind-boggling, especially when it is compared to other forms of land transport. Trucks, for instance, consume up to four times more fuel per ton-mile than railroads. There are two big drivers of this sustainability magic: individual trains can carry hundreds of tons of freight – trucks just don’t have that capability – and steel wheels on steel tracks are just inherently more efficient + create less friction than rubber tires on asphalt.
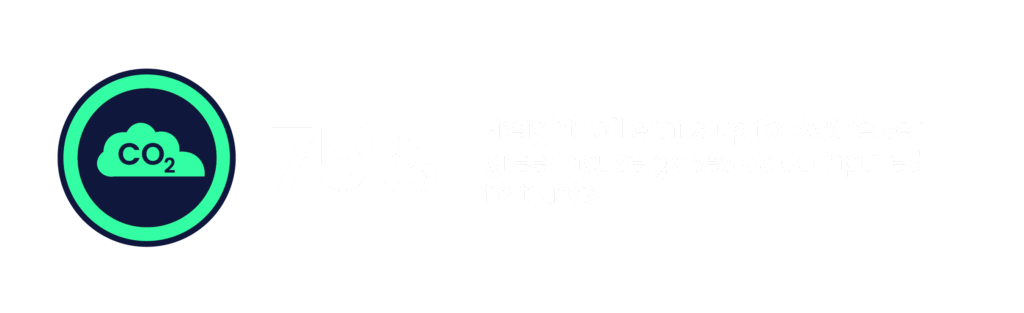
Carbon Output Matters
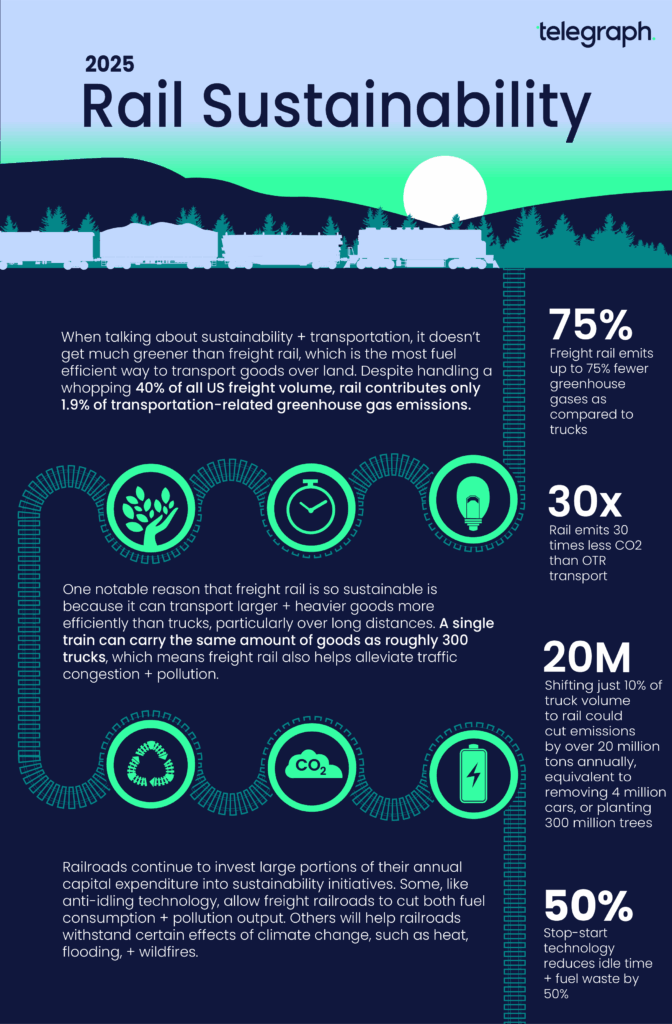
In terms of fuel consumption, railroads use significantly less fuel to transport goods over long distances. This has a direct correlation to lower greenhouse gas emissions, making freight rail a lower-carbon option as compared to other modes of transport. In fact, according to the Association of American Railroads (AAR), trains emit 75% less greenhouse gas per ton-mile as compared to trucks.
Lowering greenhouse gas emissions has actually been a long-term strategy for the railroad industry. Since 1980, railroads have reduced their overall level of greenhouse gas emissions by 40%, thanks in large part to innovative breakthroughs in locomotive technology + operational efficiencies. In addition to industry-led initiatives, government regulations have also played a role in shaping how railroads think about their carbon output. Since the 1990s, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set stringent emissions standards for railroads, particularly related to regulating locomotive emissions in order to improve air quality. California has also implemented legislation that would require zero-emissions locomotives by 2035.
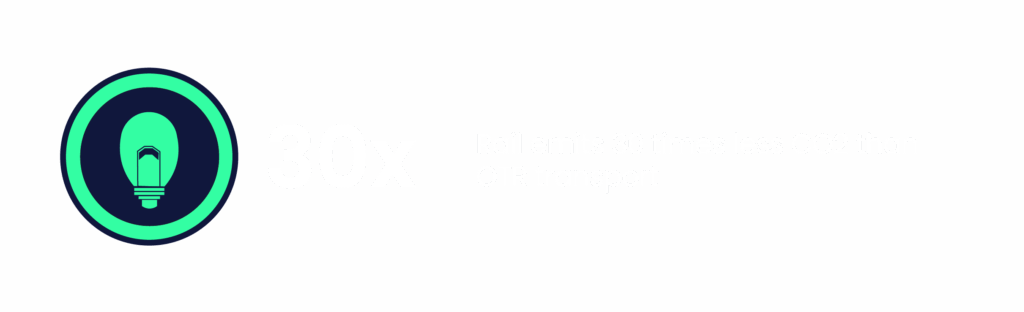
Reduced Highway Congestion
In probably the most tangible example for everyday life, railroads also benefit the environment by alleviating highway congestion + reducing the need for road repairs. According to the AAR, every ton of freight moved by rail helps reduce highway congestion by about one truck. Because each train has the ability to transport hundreds of trucks-worth of goods, a single freight train inadvertently replaces hundreds of trucks on the highway, which leads to less traffic congestion + reduced wear + tear on infrastructure. With fewer trucks on the highway, roads are maintained at a lower cost, and there is less need for new highways or traffic lanes to accommodate growing freight demand.
Rail Tech + Innovation
Technological innovation is at the forefront of everything + that includes the quest for sustainable solutions. Freight railroads recognize this, and have taken steps to ensure they are optimally utilizing technology to help meet their own sustainability targets. Locomotives are quite literally the powerhouse of railroads, and if there is room for sustainability improvements, they are a great candidate. Modern locomotives are already significantly more fuel-efficient than older models, but with further enhancements, like hybrid-electric + battery-powered locomotives, fuel consumption (and thereby emissions) are expected to drop even further. Some railroads, like CPKC, CSX, + Sierra Northern, are even testing hydrogen-powered locomotives, which could completely eliminate the need for diesel fuel entirely!
Railroads are also employing innovative anti-idling technology, or Automatic Engine Start-Stop (AESS), which automatically powers down locomotives when they are not in use + then starts them back up when they are needed. Union Pacific has launched an Energy Management System (EMS), which they liken to intelligent train cruise control – by analyzing both the train itself + the terrain it is traversing, it then optimizes for the best train handling strategy to control throttle + dynamic braking. In 2023, this system contributed to a reduction of 247,000 metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions.
Empowering a Sustainable Supply Chain
In an era of heightened environmental awareness + growing pressure to reduce carbon emissions, freight rail is the obvious solution for sustainably transporting all manner of goods across land. Railroads are continuing to invest in sustainable initiatives, helping to build a greener future for global supply chains. When choosing rail, shippers have the opportunity to win on two fronts – reducing their transportation-related carbon footprints + taking advantage of rail’s cost effectiveness.
At Telegraph, our mission has been clear to us from the outset: harness the power of freight rail technology to create a more sustainable supply chain. Our goal is to make doing business with railroads as seamless as possible, empowering shippers to continually choose rail, thus taking advantage of the many opportunities of carbon footprint reduction that rail offers. If you’re interested in learning more about how we are doing this, schedule a demo with our team today!